A complementary 12-metal-layer analysis has confirmed the system-level benefits of this semi-damascene technology in terms of RC, power consumption and IR drop. Ru was also shown as a promising alternative for contact plugs in the middle-of-line of advanced nodes.
Alternative metallization materials such as Ru and alternative metallization approaches such as semidamascene have been intensively researched to scale the back-end-of-line (BEOL) and middle-of-line (MOL) towards the 2nm technology node and beyond.
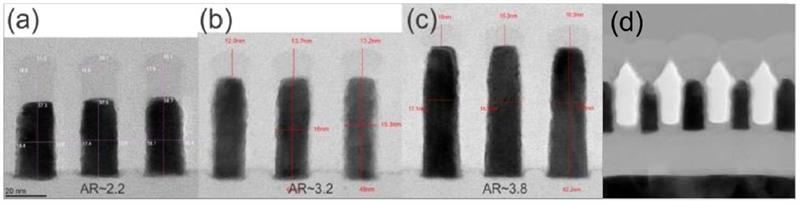
imec is proposing a semi-damascene integration for the BEOL as an alternative to traditional dualdamascene integration. To fully leverage the potential of the semi-damascene technology, metals other than Cu or Co are required that can be deposited without diffusion barrier, have a high bulk resistivity and can be patterned using e.g. subtractive etch. This allows for an increase in interconnect height which, in combination with airgaps as dielectrics, promises to reduce the resistancecapacitance (RC) delay – a major bottleneck for BEOL scaling.
Imec has also for the first time fabricated and characterized a 2-metal-level semi-damascene module on 300mm wafers using Ru for the metallization. Devices with 30nm metal pitch line test structures showed more than 80 percent reproducibility (with no evidence of shorting) and a lifetime of more than 10 years. The mechanical stability of the Ru air-gapped structures was found to be comparable to traditional Cu dual-damascene structures.
A complementary 12-metal-layer analysis revealed for the first time the system-level benefits of the semi-damascene approach in sub-3nm nodes – using a 64-bit ARM CPU as a benchmark design.Commenting Zsolt Tokei, program director nano-interconnects at imec, said, “The results show that semi-damascene in combination with airgap technology not only outperforms dual-damascene in frequency and area, it also provides a scalable path for further enhancements. Airgap shows the potential to improve performance by 10 percent while reducing the power consumption by more than 5 percent.
The use of high-aspect-ratio wires can reduce the IR drop in the power network by 10 percent to improve reliability. In the near future, a newly developed mask set for the semi-damascene module will allow us to further improve the semi-damascene integration and to experimentally validate the predicted performance improvements.”
Commenting Naoto Horiguchi, director CMOS device technology at imec said: “Alternative metals such as barrier-less Ru have the potential to further reduce the contact resistance that results from shrinking the contact area. In a benchmark study, imec evaluated both Ru and Co. The results indicate that Ru is a promising candidate for replacing Co in narrow MOL trenches.” The resistance of a Ru filled via on a 0.3nm TiN liner (without barrier) was shown to outperform the Co filled equivalent process (with 1.5nm TaN barrier). Ru as a source/drain contact material was also demonstrated, with low contact resistivity in the order of 10-9Ωcm-2 on both pSiGe and n-Si
- imec presented its findings at the 2020 International Interconnect Technology Conference.







